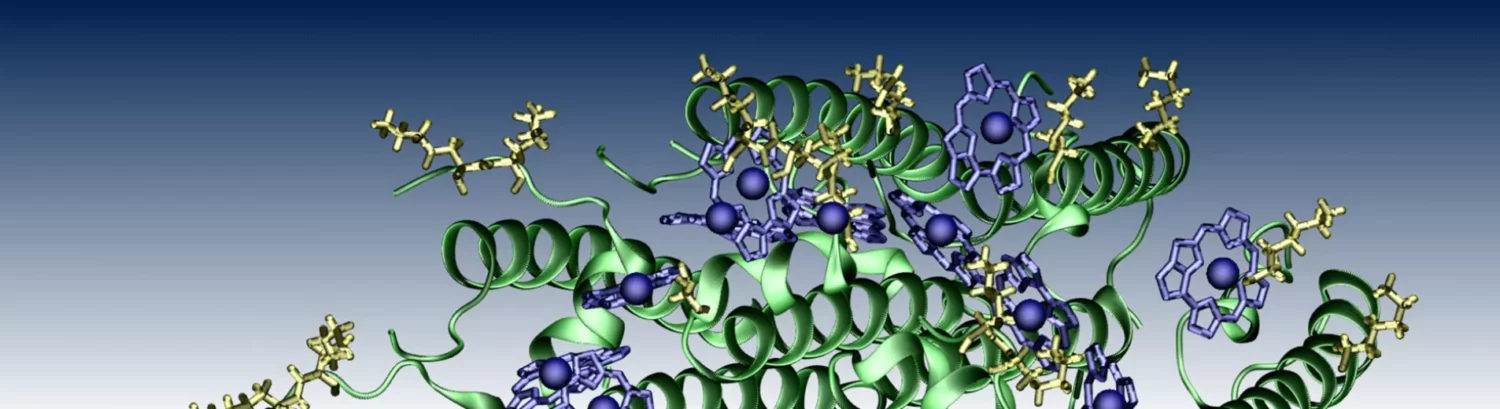
pKa prediction for LHC residues, in the presence of LHC-protein and LHC-carotenoid, lipid interactions
OneAngstrom SAS, Grenoble, France
Principal Investigator
Dr. Stephane Redon

Doctoral Candidate
Valentin Gradisteanu

Project Description:
The accurate prediction of pKa values in proteins is fundamental to our understanding of their structure, stability, and function. The protonation states of ionizable residues influence not only overall protein folding and conformational changes, but also the chemical reactivity, substrate binding, and catalytic efficiency of proteins. Determining pKa values experimentally is both time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring expensive reagents, careful experimental design, and significant labor. As a result, computational methods have emerged as powerful tools to streamline and accelerate this process.
This project, “pKa Estimations for Light Harvesting Complexes (LHC)”, aims to develop a novel computational approach that merges machine learning algorithms with core physical principles. The end goal is to significantly improve the accuracy and speed of in-silico pKa prediction, thus enabling scientists to better understand and manipulate the protonation states within complex protein systems. While the primary focus is on integrating data-driven models with physics-based concepts, the frameworks designed here could also incorporate experimental results to further refine and validate the predictive accuracy.
For Light Harvesting Complexes, which play key roles in natural and artificial photosynthetic systems, accurate pKa predictions pave the way to optimize their functionalities. By providing scientists with a versatile and efficient toolkit, this project can help accelerate innovation in both fundamental biochemical research and practical applications, benefiting fields as diverse as renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, and synthetic biology.